
Thermal energy is one of the subcategories of internal energy, as is chemical energy. The total internal energy of a system is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of its atoms and molecules. Faster moving molecules have greater kinetic energies, and so the substance has greater thermal energy, and thus a higher temperature. Without going into mathematical detail, we can say that thermal energy-the energy associated with heat-is the average kinetic energy of the particles (molecules or atoms) in a substance. Recall that kinetic energy is the energy of motion, and that it increases in proportion to velocity squared. Since heat, like work, transfers energy, it has the SI unit of joule (J).Ītoms and molecules are constantly in motion, bouncing off one another in random directions. This is because we are sensitive to the flow of energy by heat, rather than the temperature. For example, we may say that the heat was unbearable, when we actually mean that the temperature was high. Temperature is literally defined as what we measure on a thermometer. Temperature is defined in terms of the instrument we use to tell us how hot or cold an object is, based on a mechanism and scale invented by people. Heat is the transfer of energy due to a temperature difference. It is tempting to say that temperature measures heat, but this is not strictly true. What is temperature? It’s one of those concepts so ingrained in our everyday lives that, although we know what it means intuitively, it can be hard to define.
TEMPERATURE CONVERSION EQUATIONS MANUAL
In addition, the High School Physics Laboratory Manual addresses content in this section in the lab titled: Thermodynamics, as well as the following standards:

TEMPERATURE CONVERSION EQUATIONS HOW TO
Did you know that crickets can tell you how warm it is outside? Find out how to tell the temperature from cricket chirps here!
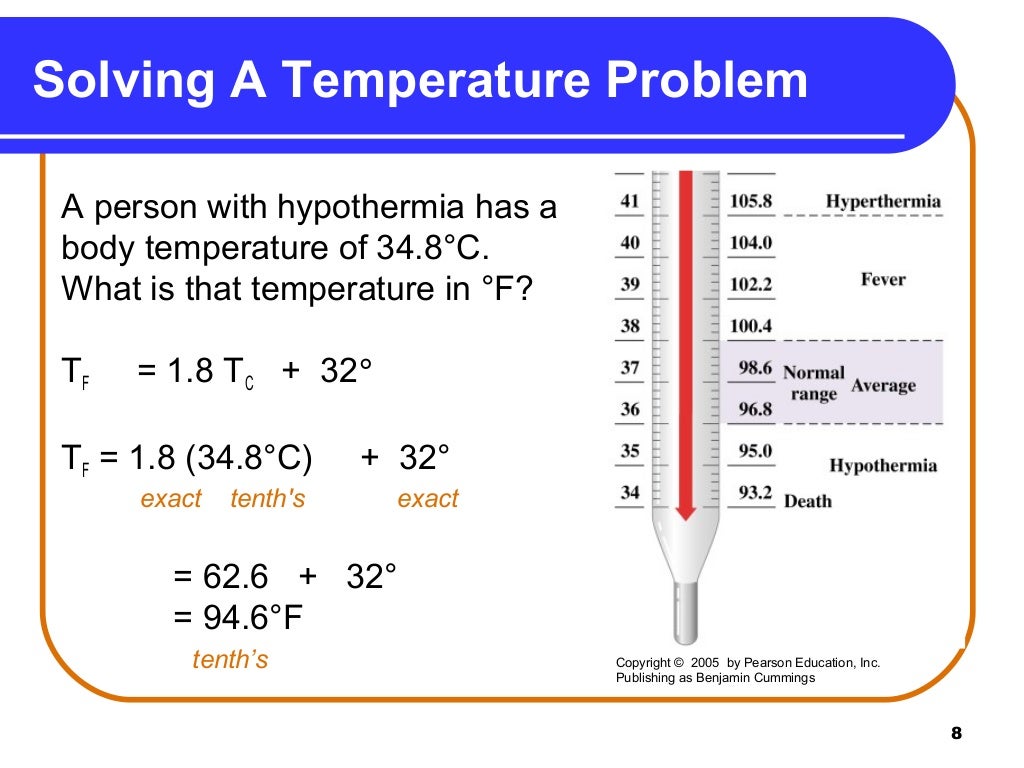

On the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32☏ and boils at 212☏ (at sea level). The Fahrenheit temperature scale is named for German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit and is the measurement of temperature commonly used by the United States (and its associated territories) and by several nations in the Caribbean. Advertisement About Fahrenheit and Celsius


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
